GLP-1(Glucagon-like peptide-1)은 인체의 중요한 호르몬으로, 혈당 조절과 식욕 억제에 핵심적인 역할을 합니다. 이 호르몬의 주요 특징과 기능에 대해 설명드리겠습니다.
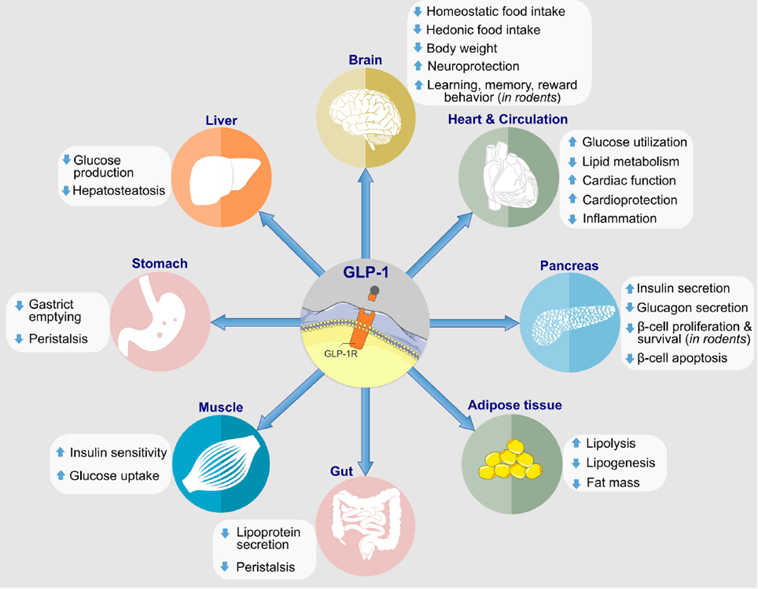
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, commonly referred to as GLP-1, is an incretin hormone primarily released in the gut in response to food intake. One of its primary biological functions is to enhance insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thus playing a crucial role in glucose metabolism. Beyond its impact on insulin, GLP-1 also inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety, which collectively aid in maintaining blood glucose levels within a normal range.
In recent years, GLP-1 has gained significant attention in the medical field, particularly for its applications in diabetes and obesity management. GLP-1 receptor agonists, a class of drugs that mimic the action of GLP-1, are increasingly used in treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. These medications help improve glycemic control by enhancing insulin secretion and reducing glucagon levels in the bloodstream, without the risk of severe hypoglycemia. Additionally, due to its ability to slow gastric emptying and increase feelings of fullness, GLP-1 therapies are also being explored for weight management in obese individuals.
The rising interest in GLP-1 has spurred extensive research, aiming to uncover further therapeutic potentials and optimize its applications. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists not only in glycemic control but also in reducing cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes. Furthermore, there is growing evidence suggesting potential benefits of GLP-1 in neuroprotection and cognitive function, opening new avenues for research in diverse health conditions beyond metabolic disorders.
As the understanding of GLP-1’s multifaceted roles in human physiology deepens, its utilization in medical treatments continues to expand, offering promising avenues for improving health outcomes in various chronic conditions. High-quality research and clinical trials remain essential in fully elucidating GLP-1’s therapeutic capabilities and ensuring optimal integration into medical practice.
GLP-1의 특성
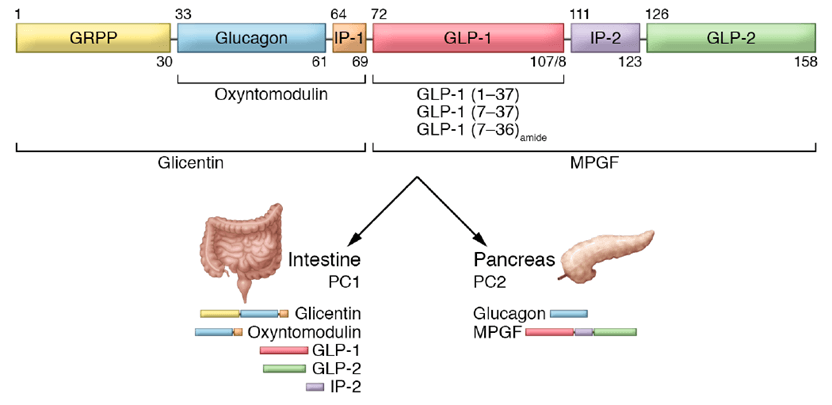
GLP-1은 주로 소장의 L-세포에서 분비되는 인크레틴 호르몬입니다. 이 호르몬은 음식 섭취에 반응하여 분비되며, 혈당 조절에 중요한 역할을 합니다.
주요 기능
혈당 조절
인슐린 분비 촉진: GLP-1은 췌장 베타 세포에서 포도당 의존적으로 인슐린 분비를 자극합니다.
글루카곤 억제: 동시에 글루카곤의 분비를 억제하여 간에서의 포도당 생성을 감소시킵니다.
식욕 및 체중 조절
위 배출 지연: GLP-1은 위 배출을 늦춰 포만감을 증가시키고 식욕을 감소시킵니다.
중추신경계 작용: 뇌의 식욕 중추에 직접 작용하여 식욕을 억제합니다.
기타 효과
인슐린 감수성 개선: 말초 조직의 포도당 흡수를 촉진합니다.
베타 세포 보호: 췌장 베타 세포의 기능을 보호하고 개선합니다.
치료적 응용
GLP-1의 이러한 특성을 활용하여 다양한 치료제가 개발되었습니다:
당뇨병 치료: GLP-1 수용체 작용제는 제2형 당뇨병 환자의 혈당 조절에 사용됩니다.
비만 치료: 식욕 억제 및 체중 감소 효과로 비만 치료에도 활용됩니다.
심혈관 질환 예방: 일부 GLP-1 제제는 심혈관 질환 예방 효과도 보고되고 있습니다.
Mechanism of Action of GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining blood glucose levels by exerting effects on several bodily processes. Produced in the intestines, GLP-1 is released in response to food intake and exerts its regulatory functions primarily through enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas, particularly after meals. This hormone achieves this by stimulating the beta cells, thereby ensuring that glucose derived from dietary sources is efficiently utilized and stored.
In addition to promoting insulin secretion, GLP-1 also inhibits glucagon release. Glucagon is a hormone responsible for stimulating the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, particularly during fasting. By suppressing this process, GLP-1 helps to lower the blood glucose levels, making it an invaluable mechanism for maintaining homeostasis.
Further, GLP-1 slows gastric emptying, which is the rate at which food exits the stomach and enters the small intestine. This slowing effect translates to a gradual absorption of glucose, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar levels post-meal. This controlled absorption is particularly beneficial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes, as it supports a more regulated and stable glucose profile.
The effects of GLP-1 are not limited to glycemic control alone. Its ability to slow gastric emptying and enhance satiety also implies potential benefits in weight management. By prolonging the sensation of fullness, GLP-1 reduces overall caloric intake, contributing to weight loss, which is a significant advantage for individuals managing obesity in conjunction with Type 2 diabetes.
These multifaceted actions make GLP-1 receptor agonists a vital therapeutic tool in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes, helping to improve both glycemic control and weight management. Understanding these mechanisms provides invaluable insights into how GLP-1-based therapies can be effectively utilized to address the complex challenges posed by Type 2 diabetes.
장점과 한계
장점
저혈당 위험이 낮음
체중 감소 효과
심혈관 및 신장 보호 효과
한계점
주로 주사제 형태로 사용됨
소화기계 부작용(오심, 구토 등)이 발생할 수 있음
GLP-1 기반 치료제는 당뇨병과 비만 치료에 혁신적인 접근을 제공하며, 지속적인 연구와 개발이 이루어지고 있습니다.
Key Statistics on GLP-1 Effectiveness
The effectiveness of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists in clinical settings is well-documented through various major clinical trials. One prominent area of improvement is in HbA1c levels, a critical marker for long-term blood glucose control. Studies have shown that GLP-1 treatments can result in a reduction of HbA1c levels by approximately 1-2%, a significant improvement for patients struggling with type 2 diabetes. This reduction is not only statistically significant but also clinically relevant, as improved HbA1c levels are closely correlated with reduced risks of diabetic complications.
Weight loss is another crucial metric where GLP-1 proves its efficacy. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that patients on GLP-1 therapy experience notable weight loss, averaging around 5-10% of initial body weight. This result is particularly important given the strong association between type 2 diabetes and obesity. By aiding in weight reduction, GLP-1 treatments not only help in better glycemic control but also alleviate the burden of obesity-related health issues.
Moreover, GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown promising outcomes in reducing cardiovascular risk factors. Significant decreases in systolic blood pressure and improvements in lipid profiles, such as lower LDL cholesterol levels and higher HDL cholesterol levels, have been observed. These changes contribute to a lower overall cardiovascular risk, which is paramount for diabetic patients who are inherently at higher risk for heart disease.
The relevance of these statistics extends to both patients and healthcare providers. For patients, the demonstrated effectiveness of GLP-1 offers a reliable option for holistic health improvements, addressing not just glucose levels but also weight and cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers can consider GLP-1 therapies as a robust option for comprehensive diabetes management plans, offering additional benefits beyond traditional treatments. Collectively, these statistics underscore the multi-faceted efficacy of GLP-1 in enhancing patient outcomes and advancing diabetic care.
Challenges and Future Directions
GLP-1 treatments, while effective in managing various metabolic disorders, come with their share of challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the side effects associated with these therapies. Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can significantly impact patient adherence. The discomfort experienced by patients often leads to discontinuation of the treatment, thereby compromising its overall effectiveness. Addressing these side effects through improved formulations or complementary medications remains a critical area of research.
Another notable challenge is the cost of GLP-1 therapies. These treatments tend to be expensive, limiting their accessibility to a broader patient population. The high cost is often a barrier for long-term treatment, raising concerns among healthcare providers and patients about the sustainability of such therapies. Efforts to reduce manufacturing costs, enhance insurance coverage, and develop more cost-effective alternatives are essential to making GLP-1 treatments more accessible.
Patient adherence is another significant obstacle. Given that GLP-1 therapies often require regular injections, maintaining consistent treatment regimens can be burdensome for patients. Advances in delivery systems, such as easier-to-use injection devices or oral formulations, are being explored to improve compliance. Researchers are also investigating the potential of sustained-release formulations, which could reduce the frequency of administration and enhance patient convenience.
Looking toward the future, ongoing research in GLP-1 therapies is promising. Scientists are exploring novel combinations of GLP-1 with other metabolic agents to enhance overall therapeutic outcomes. Emerging trends include the development of dual and triple agonists that target multiple metabolic pathways simultaneously. These advancements could potentially address some of the current limitations and offer more comprehensive treatment solutions.
Furthermore, personalized medicine approaches are being investigated to tailor GLP-1 treatments to individual patient profiles. The integration of genetic and metabolic markers could enable more precise and effective interventions. As research progresses, we anticipate significant improvements in the efficacy, convenience, and affordability of GLP-1 therapies, ultimately benefiting a wider range of patients.

GLP-1(Glucagon-like peptide-1)은 인체의 중요한 호르몬으로, 혈당 조절과 식욕 억제에 핵심적인 역할을 합니다. 이 호르몬의 주요 특징과 기능에 대해 설명드리겠습니다.
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, commonly referred to as GLP-1, is an incretin hormone primarily released in the gut in response to food intake. One of its primary biological functions is to enhance insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thus playing a crucial role in glucose metabolism. Beyond its impact on insulin, GLP-1 also inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety, which collectively aid in maintaining blood glucose levels within a normal range.
In recent years, GLP-1 has gained significant attention in the medical field, particularly for its applications in diabetes and obesity management. GLP-1 receptor agonists, a class of drugs that mimic the action of GLP-1, are increasingly used in treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. These medications help improve glycemic control by enhancing insulin secretion and reducing glucagon levels in the bloodstream, without the risk of severe hypoglycemia. Additionally, due to its ability to slow gastric emptying and increase feelings of fullness, GLP-1 therapies are also being explored for weight management in obese individuals.
The rising interest in GLP-1 has spurred extensive research, aiming to uncover further therapeutic potentials and optimize its applications. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists not only in glycemic control but also in reducing cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes. Furthermore, there is growing evidence suggesting potential benefits of GLP-1 in neuroprotection and cognitive function, opening new avenues for research in diverse health conditions beyond metabolic disorders.
As the understanding of GLP-1’s multifaceted roles in human physiology deepens, its utilization in medical treatments continues to expand, offering promising avenues for improving health outcomes in various chronic conditions. High-quality research and clinical trials remain essential in fully elucidating GLP-1’s therapeutic capabilities and ensuring optimal integration into medical practice.
GLP-1의 특성
GLP-1은 주로 소장의 L-세포에서 분비되는 인크레틴 호르몬입니다. 이 호르몬은 음식 섭취에 반응하여 분비되며, 혈당 조절에 중요한 역할을 합니다.

주요 기능
혈당 조절
인슐린 분비 촉진: GLP-1은 췌장 베타 세포에서 포도당 의존적으로 인슐린 분비를 자극합니다.
글루카곤 억제: 동시에 글루카곤의 분비를 억제하여 간에서의 포도당 생성을 감소시킵니다.
식욕 및 체중 조절
위 배출 지연: GLP-1은 위 배출을 늦춰 포만감을 증가시키고 식욕을 감소시킵니다.
중추신경계 작용: 뇌의 식욕 중추에 직접 작용하여 식욕을 억제합니다.
기타 효과
인슐린 감수성 개선: 말초 조직의 포도당 흡수를 촉진합니다.
베타 세포 보호: 췌장 베타 세포의 기능을 보호하고 개선합니다.
치료적 응용
GLP-1의 이러한 특성을 활용하여 다양한 치료제가 개발되었습니다:
당뇨병 치료: GLP-1 수용체 작용제는 제2형 당뇨병 환자의 혈당 조절에 사용됩니다.
비만 치료: 식욕 억제 및 체중 감소 효과로 비만 치료에도 활용됩니다.
심혈관 질환 예방: 일부 GLP-1 제제는 심혈관 질환 예방 효과도 보고되고 있습니다.

Mechanism of Action of GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining blood glucose levels by exerting effects on several bodily processes. Produced in the intestines, GLP-1 is released in response to food intake and exerts its regulatory functions primarily through enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas, particularly after meals. This hormone achieves this by stimulating the beta cells, thereby ensuring that glucose derived from dietary sources is efficiently utilized and stored.
In addition to promoting insulin secretion, GLP-1 also inhibits glucagon release. Glucagon is a hormone responsible for stimulating the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, particularly during fasting. By suppressing this process, GLP-1 helps to lower the blood glucose levels, making it an invaluable mechanism for maintaining homeostasis.
Further, GLP-1 slows gastric emptying, which is the rate at which food exits the stomach and enters the small intestine. This slowing effect translates to a gradual absorption of glucose, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar levels post-meal. This controlled absorption is particularly beneficial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes, as it supports a more regulated and stable glucose profile.
The effects of GLP-1 are not limited to glycemic control alone. Its ability to slow gastric emptying and enhance satiety also implies potential benefits in weight management. By prolonging the sensation of fullness, GLP-1 reduces overall caloric intake, contributing to weight loss, which is a significant advantage for individuals managing obesity in conjunction with Type 2 diabetes.
These multifaceted actions make GLP-1 receptor agonists a vital therapeutic tool in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes, helping to improve both glycemic control and weight management. Understanding these mechanisms provides invaluable insights into how GLP-1-based therapies can be effectively utilized to address the complex challenges posed by Type 2 diabetes.
장점과 한계
장점
저혈당 위험이 낮음
체중 감소 효과
심혈관 및 신장 보호 효과
한계점
주로 주사제 형태로 사용됨
소화기계 부작용(오심, 구토 등)이 발생할 수 있음
GLP-1 기반 치료제는 당뇨병과 비만 치료에 혁신적인 접근을 제공하며, 지속적인 연구와 개발이 이루어지고 있습니다.
Key Statistics on GLP-1 Effectiveness
The effectiveness of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists in clinical settings is well-documented through various major clinical trials. One prominent area of improvement is in HbA1c levels, a critical marker for long-term blood glucose control. Studies have shown that GLP-1 treatments can result in a reduction of HbA1c levels by approximately 1-2%, a significant improvement for patients struggling with type 2 diabetes. This reduction is not only statistically significant but also clinically relevant, as improved HbA1c levels are closely correlated with reduced risks of diabetic complications.
Weight loss is another crucial metric where GLP-1 proves its efficacy. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that patients on GLP-1 therapy experience notable weight loss, averaging around 5-10% of initial body weight. This result is particularly important given the strong association between type 2 diabetes and obesity. By aiding in weight reduction, GLP-1 treatments not only help in better glycemic control but also alleviate the burden of obesity-related health issues.
Moreover, GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown promising outcomes in reducing cardiovascular risk factors. Significant decreases in systolic blood pressure and improvements in lipid profiles, such as lower LDL cholesterol levels and higher HDL cholesterol levels, have been observed. These changes contribute to a lower overall cardiovascular risk, which is paramount for diabetic patients who are inherently at higher risk for heart disease.
The relevance of these statistics extends to both patients and healthcare providers. For patients, the demonstrated effectiveness of GLP-1 offers a reliable option for holistic health improvements, addressing not just glucose levels but also weight and cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers can consider GLP-1 therapies as a robust option for comprehensive diabetes management plans, offering additional benefits beyond traditional treatments. Collectively, these statistics underscore the multi-faceted efficacy of GLP-1 in enhancing patient outcomes and advancing diabetic care.
Challenges and Future Directions
GLP-1 treatments, while effective in managing various metabolic disorders, come with their share of challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the side effects associated with these therapies. Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can significantly impact patient adherence. The discomfort experienced by patients often leads to discontinuation of the treatment, thereby compromising its overall effectiveness. Addressing these side effects through improved formulations or complementary medications remains a critical area of research.
Another notable challenge is the cost of GLP-1 therapies. These treatments tend to be expensive, limiting their accessibility to a broader patient population. The high cost is often a barrier for long-term treatment, raising concerns among healthcare providers and patients about the sustainability of such therapies. Efforts to reduce manufacturing costs, enhance insurance coverage, and develop more cost-effective alternatives are essential to making GLP-1 treatments more accessible.
Patient adherence is another significant obstacle. Given that GLP-1 therapies often require regular injections, maintaining consistent treatment regimens can be burdensome for patients. Advances in delivery systems, such as easier-to-use injection devices or oral formulations, are being explored to improve compliance. Researchers are also investigating the potential of sustained-release formulations, which could reduce the frequency of administration and enhance patient convenience.
Looking toward the future, ongoing research in GLP-1 therapies is promising. Scientists are exploring novel combinations of GLP-1 with other metabolic agents to enhance overall therapeutic outcomes. Emerging trends include the development of dual and triple agonists that target multiple metabolic pathways simultaneously. These advancements could potentially address some of the current limitations and offer more comprehensive treatment solutions.
Furthermore, personalized medicine approaches are being investigated to tailor GLP-1 treatments to individual patient profiles. The integration of genetic and metabolic markers could enable more precise and effective interventions. As research progresses, we anticipate significant improvements in the efficacy, convenience, and affordability of GLP-1 therapies, ultimately benefiting a wider range of patients.
